Thanks to Life Extension for sponsoring this post. All thoughts and opinions are my own.
Collagen is a structural protein that keeps skin looking young, bones and tendons healthy and ligaments strong. You can support collagen production in the body by consuming a good-quality collagen peptide supplement along with a healthy, nutrient-rich diet. Let’s explore:
What does Collagen do in the Body?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body. Collagen is an important structural component in skin, bone, tendons and ligaments where its strength helps resist tension. This makes collagen important for strong, younger looking skin that doesn’t sag, healthy bones and tendons and stiff ligaments. Collagen is also found in lymphatic, cardiovascular, liver, lung, spleen and intestinal tissue where it is part of the structural framework.(1)
Though an important component in the body, collagen levels decrease with age due to both a decrease in collagen production and increase in collagen breakdown. In fact, adults can lose up to 1% of collagen each year!(2) This loss is probably most dramatically seen in skin tissue where the skin starts to sag and lose volume.
Improving Collagen Production
The body can make collagen by combining amino acids from protein-rich foods such as eggs, dairy, soy and beef. Vitamin C is necessary for collagen synthesis and stabilization.(3) Also, the mineral copper is critical for the enzymatic steps necessary to make collagen.(4)
Vitamin C rich foods include citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruit), tomatoes, bell peppers, cauliflower, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage and potatoes.

Copper rich foods include sesame seeds, oysters, cashew nuts, pink or red lentils, sunflower seeds, radishes, kidney beans, walnuts, Brazil nuts and chestnuts.

The protein we consume is broken down in the body into amino acids, which are used as needed. Therefore, we can eat eggs or beef and the amino acids in both foods can help build collagen. Though it may seem as if it doesn’t matter what type of protein is consumed as long as we get enough of the right type of amino acids, collagen is a unique protein supplement, unlike any other protein.
Collagen is loaded with a unique sequence of amino acids that are the building blocks of collagen in the body. These amino acids include glycine, lysine, hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine. No other protein or combination of proteins compares to collagen. Also, as we age our body becomes less efficient at relying on single amino acids from different protein sources to make collagen.
While collagen supplements can support collagen production, not all collagen supplements are the same. Due to smaller particle size, collagen peptides are absorbed directly into the small intestine, improving absorption. Collagen peptides also reduce the activity of an enzyme called metalloproteinase 2, an enzyme that breaks down collagen.(5)
How Collagen Supports Bone Integrity
Though we often think of calcium and vitamin D for their roles in bone mineral density (vitamin D is needed to help bring calcium into bones while calcium helps strengthen bone), approximately one-third of bone tissue is protein. Type 1 collagen is a major component of bone tissue and is surrounded by calcium and phosphate, which help form mineralized (hard) bone.(6,7)
It is important to build bone during adolescence and early teenage years – the peak bone building years. Though bone turnover happens throughout life where old bone tissue is replaced by new bone tissue, by the early 30s a person stops building bone density. At this point moving forward throughout life bone density can only decrease. Therefore, it is important to build and maintain peak bone density.
Tips for building strong, healthy bones:
-
- Take collagen peptides
- Engage in resistance training at least 2 times a week, preferably 3-4 times per week. This will help build up collagen in bone tissue making bones stronger.
- Consume sufficient amounts of calcium to ensure peak bone mineral density. Adults and children > 4 years of age need 1300 mg of calcium daily. Calcium rich foods include dairy (cheese, milk, yogurt, kefir), fatty fish, fortified orange juice. Leafy greens and other vegetable sources of calcium contain far less of this mineral compared to dairy foods.
- Consume enough vitamin D. Vitamin D helps promote calcium absorption. Adults and children > 4 years of age need 600 mg of vitamin D daily. Food sources of vitamin D include fatty fishes, egg yolks, cheese, fortified orange juice, and fortified milk. Some yogurts are also fortified.
- Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables for bone health – lycopene rich produce like watermelon, tomatoes, pink grapefruit, bell peppers, and papaya, as well as beta cryptoxanthin rich orange colored fruits and vegetables such as squash (including pumpkin), bell peppers, tangerines, oranges, and carrots. Lycopene has been shown to support bone health.(8) Beta cryptoxanthin has a protective effect on bone tissue.(9)
In addition to its role in bone, collagen can improve tendon health and ligament strength. For more information including how to take collagen for healthy tendons and ligaments, click here.
Improving Muscle Function with Collagen
Muscle is important throughout the lifespan. Muscle enables us to not only work out but also engage in activities of daily living including lifting a child, lifting groceries or opening a jar of food. The top thing we can do to build muscle is engage in resistance training (strength training): any activity that forces the muscles to contract against resistance. In addition to resistance training, a healthy diet helps build muscle.
Just like collagen production decreasing with age, muscle mass also declines with normal age. Inactivity and poor protein or calorie intake can all affect muscle health.(10)
Though muscle is built with complete proteins, those containing all essential amino acids, collagen has a role in muscle as well. Collagen supports the endomysium, the layer of connective tissue that covers individual muscle cells. Collagen adds structure to this connective tissue and improves muscle functioning by support muscle fiber absorption and muscle contraction.(11)
How can you support healthy muscle functioning?
- Supplement with collagen peptides
- Consume high quality, complete proteins at least 3 times a day at mealtime. A complete protein has all essential amino acids. All animal proteins are complete as is soy. Plant proteins, other than soy, must be combined to make a complete protein.
- Exercise and include resistance training in your program at least 2 days per week, preferably 3-4 days per week. Plus, switch up your exercises so you aren’t always doing the same thing day after day.
How Does Collagen Support Youthful Skin?
Have you wondered why skin changes throughout the lifespan? Young children have a clear canvas typically uniform in color. With normal age, skin thins, and loses moisture.
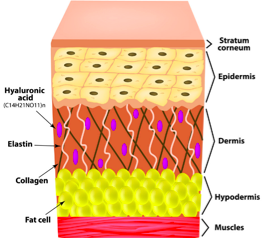
The second layer skin tissue, the dermis, is composed of collagen, elastin and hyaluronic acid. Collagen provides strength and structure to the skin while elastin provides elasticity. As we age, collagen production declines by about 1% per year and skin starts to sag.2 Skin that has been exposed to environmental exposure has decreased collagen content likely due to greater collagen breakdown. In aged skin, collagen also looks disorganized.(12)
In addition to a decline in collagen production with age, there is also an increase in enzymatic breakdown of collagen, increased glycation and increased transdermal water loss. All of these factors contribute to older looking skin.
In addition to collagen, hyaluronic acid helps skin retain healthy moisture. In fact, 50% of the body’s hyaluronic acid is found in the skin where it is an essential component of the structurally important space between cells throughout the body. Supplementing with hyaluronic acid helps stimulate HA synthesis, restoring youthful levels of this essential compound and encouraging healthy skin hydration. Hyaluronic acid is relatively rare in foods though it is found in organ meats, bone broth and collagen.(13) Luckily, both collagen and hyaluronic acid are in Life Extension’s Gummy Science™ Youthful Collagen gummies which have zero added sugar, so you get all the skin-nourishing goodness without ingredients you don’t want! Gummy Science™ Youthful Collagen gummies contain clinically studied dosages of 2500 mg of VERISOL® Bioactive Collagen Peptides® and 120 mg of hyaluronic acid. These gummies support healthy skin hydration, smooth the appearance of wrinkles and support skin elasticity.
VERISOL® collagen is an ultra-bioavailable form of type 1 collagen that is absorbed as both free amino acids and as intact collagen peptides that are transported directly to your thirsty skin. VERISOL® collagen stimulates the formation of new collagen, as well as elastin, a molecule in your skin that helps keep it smooth and supple.
Compared to placebo, VERISOL® collagen showed considerable improvement in skin elasticity levels after just 4-8 weeks of once-daily supplementation.(14) VERISOL® collagen also produced a dramatic 20% reduction in the volume and appearance of eye wrinkles after just 8 weeks (compared to placebo).(15)
There are several things you can do to support the texture of skin:
- Consume a collagen peptide supplement to support collagen synthesis and modulate enzymatic breakdown of collagen. Consuming collagen peptides will result in skin that looks more youthful.
- Consume a hyaluronic acid supplement for healthy skin moisture. Life Extension’s Gummy Science™ Youthful Collagen gummies make it easy to get both collagen and hyaluronic acid.
- Use a good quality, broad-spectrum sunscreen every day (even in the winter) to help minimize environmental exposure.
- Consume a diet rich in fruits and vegetables to help maintain youthful skin.(16) Be sure to focus on vitamin C-and copper-rich foods.
- Watch sugar intake. Excess sugar binds to collagen in a reaction called glycation. This can affect the structure and function of collagen.
Collagen is an important structural protein in bone, tendons, ligaments, muscle and skin health. Though you can find collagen in food sources like bone broth, collagen peptide supplements are more easily absorbed than other forms of collagen. A healthy, plant-based diet is also critical for collagen formation and decreasing collagen breakdown in the body. In particular, a diet containing plenty of vitamin C-rich foods as well as copper-rich foods supports collagen synthesis in the body. Also, along with collagen, calcium, vitamin D and other bone building nutrients, food sources of lycopene and beta cryptoxanthin (found in many fruits and vegetables) support healthy bone. Lastly, staying well hydrated and well rested will improve skin texture.
VERISOL® and Bioactive Collagen Peptides® are registered trademarks of GELITA AG.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
1 Shuster S, Black MM, McVitie E. The influence of age and sex on skin thickness, skin collagen and density. Br J Dermatol 1975; 93(6):639-43
2 Peterkofsky B. Ascorbate requirement for hydroxylation and secretion of procollagen: relationship to inhibition of collagen synthesis in scurvy. Am J Clin Nutr 1991;54(6 Suppl):1135S-1140S.
3 Borkow G. Using Copper to Improve the Well-Being of the Skin. Curr Chem Biol 2014; 8(2): 89–102.
4 Shoulders MD, Raines RT. Collagen structure and stability. Annu Rev Biochem 2009; 78: 929–958.
5 Zague V, de Freitas V, da Costa Rosa M, de Castro GA, Jaeger RG, Machado-Santelli GM. Collagen hydrolysate intake increases skin collagen expression and suppresses matrix metalloproteinase 2 activity. J Med Food 2011;14(6): 618-24.
6 Tzaphlidou M. Bone Architecture: Collagen Structure and Calcium/Phosphorus Maps. J Biol Phys 2008; 34(1-2): 39–49.
7 Ritchie RO, Buehler MJ, Hansma P. Plasticity and toughness in bone. Physics Today 2009;41-46.
8 Sahni S, Hannan MT, Blumberg J, Cupples LA, Kiel DK, Tucker KL. Protective Effect of Total Carotenoid and Lycopene Intake on the Risk of Hip Fracture: A 17-Year Follow-Up From the Framingham Osteoporosis Study. J Bone Miner Res 2009; 24(6): 1086–1094.
9 Yamaguchi M. Role of carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin in bone homeostasis. J Biomed Sci 2012; 19(1): 36.
10 Bone Health and Osteoporosis. A Report of the Surgeon General. Office of the Surgeon General (US). Rockville (MD): Office of the Surgeon General (US); 2004.
11 Gillies AR, Lieber RL. Structure and Function of the Skeletal Muscle Extracellular Matrix. Muscle Nerve 2011; 44(3): 318–331.
12 Ganceviciene R, Liakou AI, Theodoridis A, Makrantonaki E, Zouboulis CC. Skin anti-aging strategies. Dermatoendocrinol 2012; 4(3): 308–319.
13 Kawada C, Yoshida T, Yoshida H, Matsuoka R1, Sakamoto W, Odanaka W, Sato T, Yamasaki T, Kanemitsu T, Masuda Y, Urushibata O. Ingested hyaluronan moisturizes dry skin. Nutr J 2014;13:70.
14 Proksch E, Segger D, Degwert J, Schunck M, Zague V, Oesser S. Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has beneficial effects on human skin physiology: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 2014;27(1):47-55.
15 Proksch E, Schunck M, Zague V, Segger D, Degwert J, Oesser S. Oral intake of specific bioactive collagen peptides reduces skin wrinkles and increases dermal matrix synthesis. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 2014;27(3):113-9.
16 Mekić S, Jacobs LC, Hamer MA, Ikram MA, Schoufour JD, Gunn DA, Kiefte-de Jong JC, Nijsten T. A healthy diet in women is associated with less facial wrinkles in a large Dutch population-based cohort. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019;80(5):1358-1363.
Collagen is indeed important for overall health and beauty.This is informative post i really like the way it is written